Port Management
View and manage processes using network ports.
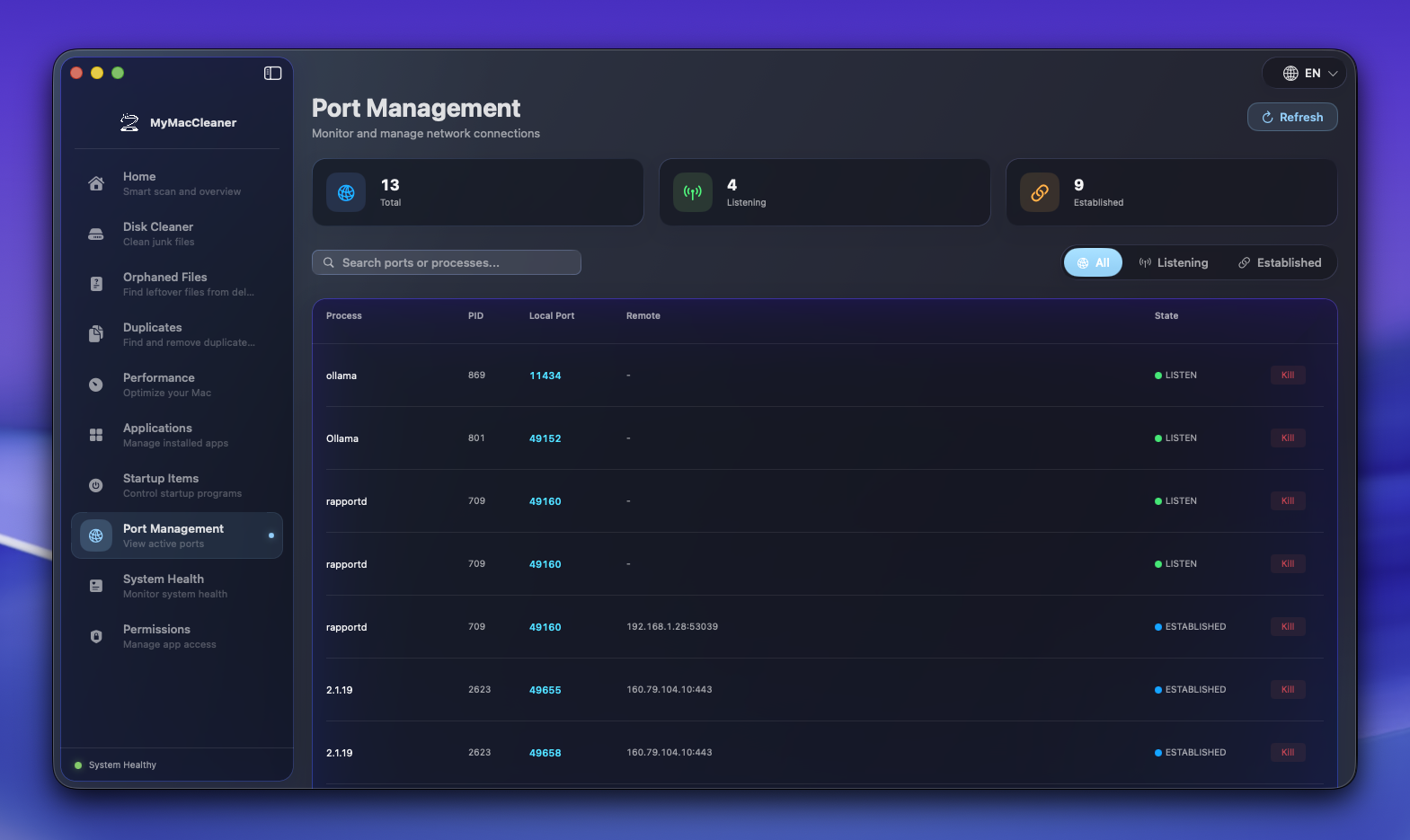 Port Management showing active network connections and listening ports
Port Management showing active network connections and listening ports
Overview
Port Management helps developers and power users see what’s running on their Mac’s network ports and terminate processes when needed.
Understanding Ports
What is a Port?
A port is a communication endpoint. When applications need network access, they “listen” on specific ports:
- Port 80 - HTTP web traffic
- Port 443 - HTTPS secure web traffic
- Port 22 - SSH connections
- Port 3000 - Common development server port
- Port 8080 - Alternative HTTP port
- Port 5432 - PostgreSQL database
- Port 3306 - MySQL database
- Port 27017 - MongoDB database
Connection States
| State | Meaning |
|---|---|
| LISTEN | Waiting for incoming connections |
| ESTABLISHED | Active connection |
| TIME_WAIT | Connection closing, waiting to ensure delivery |
| CLOSE_WAIT | Remote side closed, waiting for local close |
| CLOSED | Connection terminated |
Interface
Connection Table
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Port | Local port number |
| Process | Application name |
| PID | Process ID |
| Protocol | TCP or UDP |
| State | Connection state |
| Remote | Remote address (if connected) |
| Actions | Kill button |
Toolbar
- Search - Filter by port number or process name
- State Filter - Show only specific states
- Refresh - Update connection list
- Auto-refresh - Toggle automatic updates
Common Tasks
Find What’s Using a Port
- Open Port Management
- Enter port number in search (e.g., “3000”)
- See the process using that port
Kill a Process by Port
- Find the connection in the list
- Click Kill button
- Confirm the action
- Process terminated
View All Listening Ports
- Set State filter to “LISTEN”
- See all services waiting for connections
- Useful for security audits
Kill Options
Graceful Termination (SIGTERM)
- Default option
- Allows process to clean up
- May fail for stuck processes
Force Kill (SIGKILL)
- Immediate termination
- No cleanup opportunity
- Use when graceful fails
- May cause data loss
Common Port Conflicts
Development Servers
Problem: “Port 3000 already in use”
Solution:
- Find process using port 3000
- Kill it or use different port
- Restart your development server
Database Connections
Problem: Can’t connect to database
Check:
- Is database server running?
- Is it listening on expected port?
- Any firewall blocking?
Zombie Processes
Problem: Port shows in use but app closed
Solution:
- Find the orphaned process
- Force kill it
- Port now available
Safety Warnings
System Processes
Some processes are critical:
- launchd - System process manager
- kernel_task - Core system process
- WindowServer - Display server
Never kill these - may require restart.
Protected Ports
Ports below 1024 are “privileged”:
- Require root access to bind
- Usually system services
- Kill with caution
Command Line Equivalent
MyMacCleaner uses these commands internally:
# List all connections
lsof -i -P -n
# Find specific port
lsof -i :3000
# Kill process by PID
kill -15 <PID> # Graceful
kill -9 <PID> # Force
# Kill process on port (one-liner)
kill -9 $(lsof -t -i:3000)Tips
- Development workflow - Keep Port Management open while coding
- Port conflicts - Check before starting new services
- Security - Review unknown listening processes
- Debugging - Verify services are running on expected ports
Keyboard Shortcuts
| Shortcut | Action |
|---|---|
Cmd + R | Refresh list |
Cmd + F | Focus search |
Cmd + K | Kill selected process |
Cmd + C | Copy process info |